Wind Turbine Blades
With increased demand for electricity and the global move towards renewable energy sources wind turbines are becoming increasingly popular. The wind turbines are mostly located off-shore or in remote, rural on-shore locations. With rotor diameters now often exceeding 133 metres and towers more than 100 metres tall, any damage sustained by these structures will have severe financial consequences related to access, replacement/repair and business interruption cost. Wind turbine blades are the largest single element of a wind turbine and are they logistically difficult to deal with.
The outer ‘skins’ of the blades are typically made from several layers of fibre-reinforced composite materials. Internal stiffening ‘rods’ are also commonly made from composites. The complexity of composite material manufacturing and the size of a blade increases the risk of manufacturing defects. In addition, the height of the structure and location of the turbines puts them at risk of damage from extreme weather events, such as lightning strikes or storm damage.
There are also logistical difficulties with the transportation and installation of blades. Their size and weight, combined with the typical remote locations of wind farms (whether on-shore or off-shore) means that transporting them comes with numerous challenges. In addition to size and weight concerns, the aerodynamic importance of wind turbine blades’ shape and their surface finish means that blade damage during transport and installation are significant concerns.
WHY APPOINT A FORENSIC INVESTIGATOR?
If you are dealing with an engineering failure and want to identify the root cause, how it happened and how to prevent it from recurring, a forensic investigator can help. Hawkins can provide an expert who is familiar with all aspects of a case and can offer clarity and answers to your questions.
- Our experts have in-depth knowledge of composite materials, and extensive experience of the manufacturing techniques and structures of wind turbine blades.
- We can utilise, or recommend non-destructive testing techniques to analyse the condition of wind turbine blades and similar structures.
- Our experts can analyse operations data from advanced systems such as SCADA systems, or vibration monitoring. These systems often enable our experts to provide advice on maintenance, or related issues.
- Our experts can obtain critical evidence regarding the failure of a wind turbine blade from visual examination.
- We have experts with suitable qualifications for working at height and offshore.
We have experience of all major manufacturers and with turbines of all ages and sizes.
We have extensive knowledge and experience from which to undertake sampling of a damaged or failed blade, from which to conduct laboratory-based examinations, tests and analyses.
Our investigations can identify the root cause of the failure or the damage.
- We have extensive experience in supporting subrogation or recovery efforts.
We provide the technical and scientific advice you need to make decisions including where legal responsibilities and liabilities lie.
We have provided court reports and given evidence in numerous international court cases, and in many regions around the world.
Our experts’ knowledge of manufacturing techniques, non-destructive testing, operating data analysis and the vulnerabilities of wind turbine blades (and similar structures) enables us to provide sound expert advice on risk-minimisation and prevention of future failures.
We have extensive experience of repair processes, providers and we can provide expert support and advice to obtain the best possible outcome after damage or a failure.
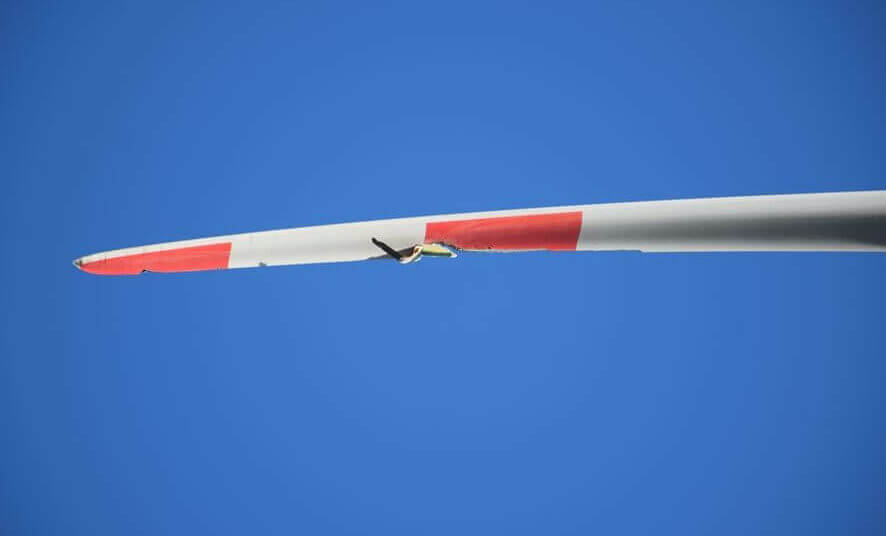


Examples of typical cases
- Blade fracture
- Cracks at various locations of the blade
- Blade surface damage
- Adhesive damage / failure
- Lightning strike
- Other storm damage
- Transport and installation damage
These are just some of the types of wind turbine failures that we can investigate.
If you need help to determine the cause of an issue or in establishing liability, call us for a free consultation or fill out our enquiry form.
HOW DOES HAWKINS INVESTIGATE ENGINEERING FAILURES AND LOSSES?
1
Consultation
When we receive an enquiry about a wind turbine blade failure or damage, the provision of data and background information can be crucial for identifying the best way to undertake an investigation. Photographs of the damage, video footage of the incident and witness information help us to understand the likely nature of the failure. Operating data, and the repair and maintenance history for the turbine can provide critical clues regarding potential causes, and comparative data for other, neighbouring turbines can highlight local or widespread concerns.
2
Inspection
Travelling to site to inspect the failed or damaged wind turbine blade will enable our expert engineer to assess the extent and nature of the damage, and to locate and analyse the source, or origin of the failure. An on-site inspection also enables us to consider any potentially relevant factors in the local environment. Often, further inspections of samples or specimens taken from a blade, in a suitable workshop or laboratory, will be required for us to fully analyse the detail and establish the root cause of the failure.
3
Conclusion
After the inspections and laboratory work, we can produce a detailed and illustrated report, summarising the work completed and explaining the key findings and conclusions of our investigation. This can include advice on operational or inspection procedures, to minimise the risk of similar, future failures, if required.
SPEAK TO ONE OF OUR EXPERTS
Principal Associate, Managing Director (Acoustics)
Email meRelated areas of expertise
Boilers and Heat Recovery Steam Generators
Boilers, essential for power, vary in size and face issues like water control problems and corrosion, leading to failures. Checking boiler tubes during yearly inspections is crucial, as tube replacement is time-consuming. Shifting to renewable fuels like wood poses challenges, such as fireside corrosion due to aggressive flue gases.
Gas Turbines
Gas turbine failures can result in financial losses of tens or even hundreds of millions of pounds. Failures can range from simple mechanical issues with valves or ducts to more complex issues such as blade failure, bearing failure or an instability with airflow and combustion.
Solar
In recent years, solar photovoltaic power has become increasingly affordable, prompting numerous UK and global projects. Common issues involve inverter panel and electrical failures. Solar thermal, with smaller global capacity, faces challenges like heat exchanger issues and frequent start-stop operations impacting steam turbines and generators.