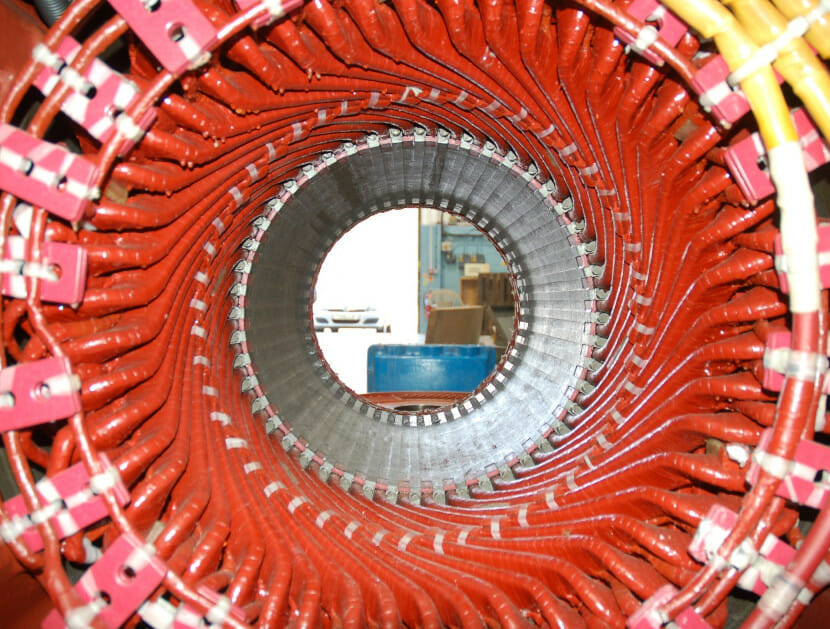
Gas Turbines
Gas turbine engines vary in size from micro (20-350 kW) to large industrial units (590 MW) and remain the product of choice for many operators worldwide in the power and energy industry.
The operational flexibility, efficiency and reliability make them ideally suited for use both offshore and on land. Also, with the transition to green energy, gas turbines play an ever more crucial role in supporting power grids and as replacements for retiring coal-fired generation.
However, this sophisticated equipment can and does occasionally fail, potentially resulting in financial losses of tens or even hundreds of millions of pounds. Failures can range from simple mechanical issues with valves or ducts to more complex issues such as blade failure, bearing failure or an instability with airflow and combustion. In providing a supporting role to renewable generation, gas turbine operation is transitioning further towards rapid starts and relatively short periods of operation, which have a detrimental effect on the life of many components, and can impact reliability and maintenance intervals.
Failure to meet contractual requirements in terms of performance, emissions or maintenance schedule is also a common complaint from operators.
Despite the significant technical challenges that remain, gas turbines will also be increasingly used for burning renewable fuels such as hydrogen. As with all new technology, there will almost certainly be reliability challenges and failures along the way, but the gas turbine market will continue to grow into the foreseeable future and “keep the lights on” for many years to come.
WHY APPOINT A FORENSIC INVESTIGATOR?
Our team of experts can assist you in identifying the root cause of component failures and operational issues and support you in returning the asset to service as quickly as possible.
We also have expertise and practical experience to impart the best practice guidance in this sector to reduce the risk of failure.
- We have decades of experience working as operators of power plants or providing expert advice to operators, from new build, operations, and life extension to end of life.
- We can advise on international best practice for the operation and maintenance of generators.
- We can support with condition monitoring, health assessments, and analysis of test results to provide the owner and operator an independent assessment of their asset, empowering them in discussions with vendors and OEMs.
- Our experts are well versed in all areas of gas turbine manufacture and operation, failure modes and data analysis.
- We have experience of working on gas turbines from all the main OEMs and many of our experts have previously worked for these companies and associated industries.
- We have well equipped metallurgical laboratories with state of the art digital microscopy and access to the latest electron microscopy.
- We have a deep understanding of power plant operation.
- We carry out damage assessments to advise insurers on the repair scope, and the effect of future operation and overhauls, in relation to the damage caused during an incident.
- We support subrogation/recovery efforts.
- We help you to make decisions regarding where legal responsibilities and liabilities lie.
- We have provided court reports and given evidence in international court cases.
- We provide consultancy advice to prevent similar events.
- We can support the repair and restoration of turbines, suggesting repairs and service providers.

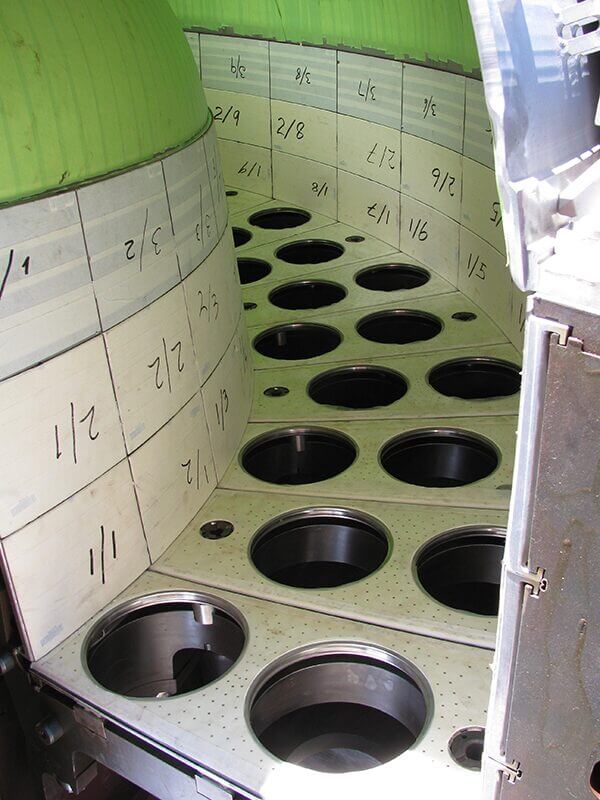
Examples of Typical cases
- Root cause analysis of operational failures
- Compressor and turbine blade failures
- Thermal barrier and other coating failures
- High vibration problems
- Performance degradation
- Bearing failures
- Control system issues
- Combustion problems
- Package issues
- Metallurgical failures
- Support to operators or new projects and assistance with discussions with OEMs and second tier service and parts providers.
- Critical spares/ risk based inspections
- Condition assessment and life assessment
- Fires
If you would like to discuss how we can assist you please fill out our enquiry form or call us for a free consultation.
HOW DOES HAWKINS INVESTIGATE GENERATOR FAILURES?
1
Consultation
On receipt of the enquiry, we like to speak with you before we conduct any work, to obtain the background information.
These discussions help us to understand your requirements, as well as determine how much information is already available, including for example, service records, first-hand witness accounts, photographs, and videos.
We are also happy to provide you with an estimate of the cost of conducting a forensic investigation.
2
Inspection
If required and with your agreement, we will arrange to examine the relevant equipment, either on-site or at a workshop, to establish the facts regarding the failure and the circumstances surrounding it.
This usually involves taking witness statements, examining physical evidence and studying engineering drawings, specifications and manuals.
Wherever possible, we will retain faulty parts for examination in our laboratory, where we use a range of equipment, tools, and tests. Where a dispute remains or where facts are not available, we will provide an informed and professional opinion.
3
Reporting
Once our examination is complete, we will discuss our findings with you and prepare a report containing a detailed account of our investigation, conclusions, and where appropriate, further work or advice.
We are independent, impartial and unbiased and we are instructed by both Claimant and Defendant solicitors and insurers. We are flexible in terms of reporting and we work within the relevant Civil Procedure Rules and are effectively agents of the Court in everything we do.
SPEAK TO ONE OF OUR EXPERTS
Testimonial
“Thank you for your superb effort in this case.”
Rhys Phillips
“Many thanks for turning out today at such short notice and providing the benefit of your expertise and knowledge. It was evident the Client was extremely relieved that this matter was being investigated expeditiously.”
Chaz Winterton
“I just wanted to say thank you for all your help and the information you found was of real insight. Thank you again for all your help.”
Stewart Hargreaves
“I just wanted to say thank you for all of your hard work preparing the Hawkins report. Please pass on my thanks to the rest of the team. We really appreciate the hours you have all put in and I know the client is pleased with your work.”
Philippa Jones
“I have recently needed structural engineering opinion on one matter and geotechnical engineering opinion on another. I experienced the usual difficulties with traditional providers of those services – excessive cost, inability to get on site quickly etc etc. When turning to Hawkins the contrast was clear – economical pricing, fantastic turnaround times, and really helpful reports that focussed on my needs without me needing to spend ages spelling it all out.”
Hawkins client
Related areas of expertise
Power & Energy
Hawkins' power experts have experience of forensically investigating losses worldwide on a wide range of power generation equipment from traditional thermal and nuclear power plants through to wind, hydro and solar generation as well as emerging technologies such as battery and flywheel installations.
Electrical Engineering
With the prevalence of electrical and electronic devices in the modern world there is considerable scope for failures to occur. These can range from the failure of a single electronic component to failure of multi-megawatt power plants.
Hydro Power
Hydro power generation was the first green renewable energy and battery storage facility. Hawkins forensic investigators have completed numerous investigation into hydro power plant failures.
Geothermal
Geothermal power systems rely on the use of steam/hot water generated by the heat within the Earth’s crust and as such, the working media is significantly more aggressive than conventional steam systems. This results in more issues with corrosion and scale formation which affects the availability and utilisation of the power generation asset or heat exchanger unit.