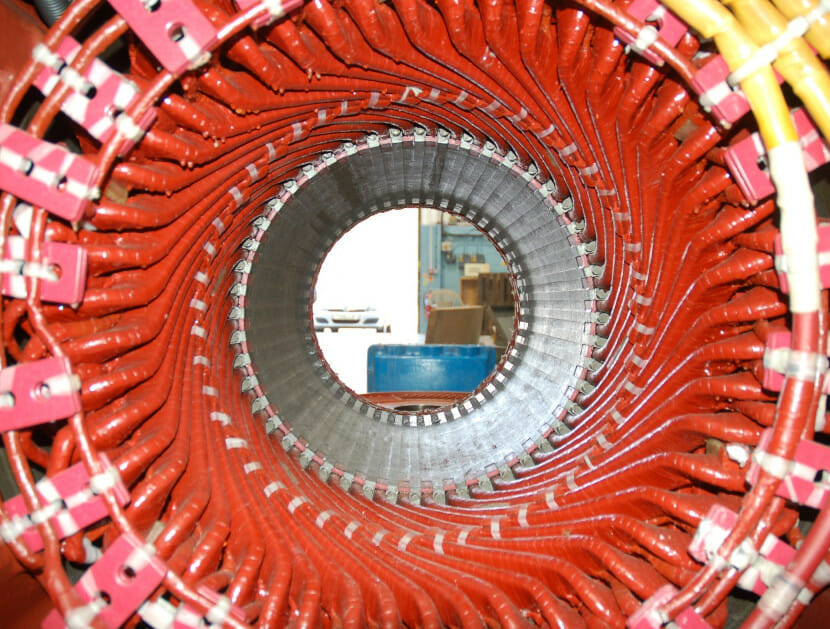
Subsea Power Cables
All offshore renewable power generation relies on subsea power cables, including offshore wind, wave, tidal and solar power. Subsea power cables fall into the following broad categories:
Interconnectors
- Long distance High Voltage DC (HVDC), voltages e.g. 400 kV - 500 kV, power up to 2 GW.
- Shorter distance High Voltage AC (HVAC) e.g. 420 kV.
- Used for large-scale power transmission between national grids.
Export Cables
- HVAC or HVDC depending on distance (crossover from HVAC to HVDC is about 80km.)
- Typical offshore wind voltages 210, 230, 275 kV (AC) and 320 kV (DC).
- Used for export from wind farms, solar/PV farms and tidal stream systems.
Inter-Array Cables
- Medium Voltage AC (MVAC), typically 33kV, 66kV (but already increasing to 132kV HVAC).
- Shorter length cables but many of them.
- Used in offshore wind farms (fixed-bottom and floating) and for smaller export requirements e.g. from wave energy devices.
Subsea power cables are multi-layered polymer/metal structures consisting of cylinders and helically wound strips or wires. AC cable cores consist of three multi-layered cables wound together helically. Some of these layers are delicate and are at risk of damage during transportation, installation and operation. The cables operate in harsh, dynamic environments, and cable systems need careful design to mitigate the threats from wear and fatigue at exposed locations, usually near the cable ends.
WHY APPOINT A FORENSIC INVESTIGATOR?
Our team of experts have both the expertise and practical experience to impart best practice guidance in this sector to reduce the risk of failure.
If a failure does occur, Hawkins can assist you in identifying the root cause of the issue and support you in reducing the risk of repeat failures. We can also provide advice on repair scope and procedures.
- We have in-depth understanding of cable mechanical behaviour and cable dynamic response modelling.
- We can advise on the suitability of cable loadout, transport and installation procedures.
- We can advise on subsea power cable system condition monitoring.
- We can perform detailed layer-by-layer cable dissection or dissection witnessing.
- We have experience in cable failure root cause analysis.
- We support subrogation/recovery efforts.
- We help you to make decisions regarding where legal responsibilities and liabilities lie.
- We can provide advice on root cause analysis and mitigation against further failures in existing infrastructure.
- We can advise on the design of replacement systems to prevent failure recurrence.
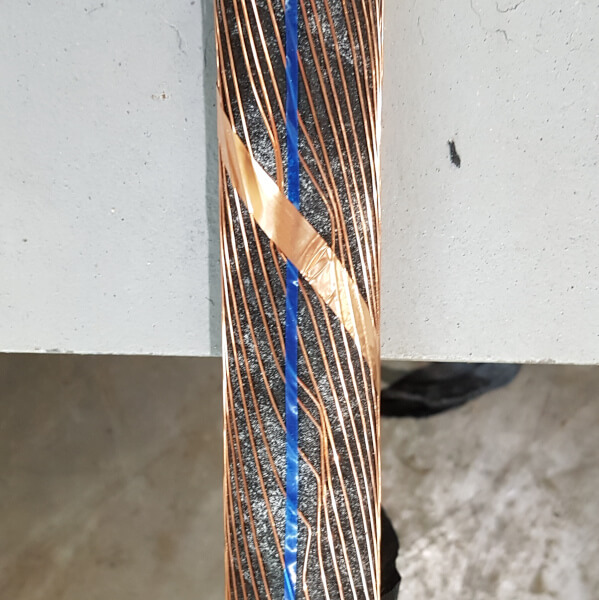
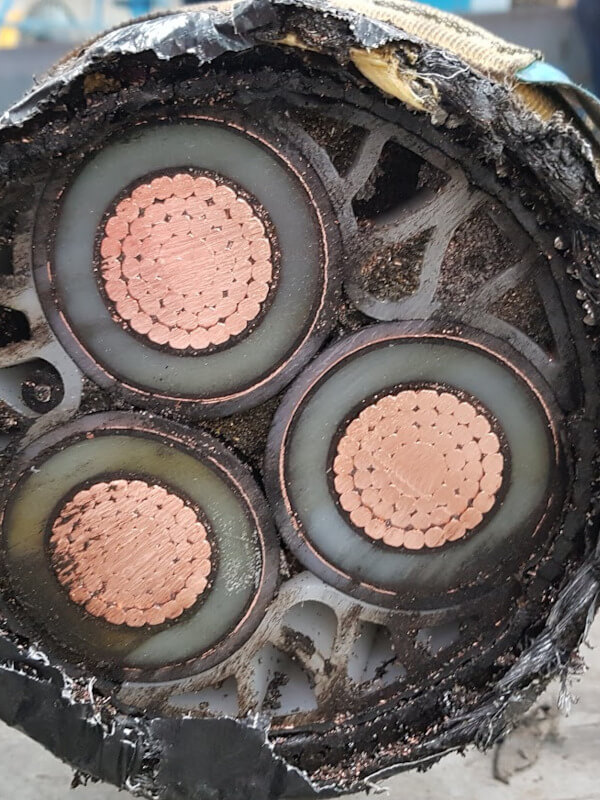


Examples of Typical cases
The list below provides a few examples of the types of incidents we regularly investigate or have experience with:
- Screen and sheath fatigue
- Armour birdcaging
- External wear
- Cable protection system failures
- Joint failures – water ingress or loss of layer integrity
- Cable looping
- Cable coiling damage
If you would like to discuss how we can assist you please fill out our enquiry form or call us for a free consultation.
HOW DOES HAWKINS INVESTIGATE SUBSEA POWER CABLE FAILURES?
When Hawkins is requested to investigate an issue we employ in-house methodology built from over 40 years of experience. This enables all Hawkins investigators to provide a consistency of service and product. The methodology comprises three steps:
1
Consultation
On receipt of the enquiry, we discuss with the instructing party what happened and when it happened. We also request all available data covering cable and system design, and operation and maintenance records of the cable during its operating life. Operational data before and during the failure event will be requested. We may also interview personnel on duty at the time of the failure to get an insight into the timeline of events before, during and after the failure.
2
Inspection
Following collection of all the data and completion of the consultation, Hawkins engineers will travel to inspect the recovered asset. Support for the recovery operation itself can also be provided. Inspection will enable us to assess the extent of the damage and assist in identifying the root cause of the failure. This step may require samples to be removed and examined in one of our laboratories.
3
REPORTING
On completion of the inspection, a detailed report will be issued summarising the work completed and the findings of the investigation. The report can include advice on changes to system design, operation and inspection to minimise future events.
SPEAK TO ONE OF OUR EXPERTS
Testimonial
“Thank you for your superb effort in this case.”
Rhys Phillips
“Many thanks for turning out today at such short notice and providing the benefit of your expertise and knowledge. It was evident the Client was extremely relieved that this matter was being investigated expeditiously.”
Chaz Winterton
“I just wanted to say thank you for all your help and the information you found was of real insight. Thank you again for all your help.”
Stewart Hargreaves
“I just wanted to say thank you for all of your hard work preparing the Hawkins report. Please pass on my thanks to the rest of the team. We really appreciate the hours you have all put in and I know the client is pleased with your work.”
Philippa Jones
Related areas of expertise
Power & Energy
Hawkins' power experts have experience of forensically investigating losses worldwide on a wide range of power generation equipment from traditional thermal and nuclear power plants through to wind, hydro and solar generation as well as emerging technologies such as battery and flywheel installations.
Drains, Sewers & Septic Tanks
Few of us like to think too much about how wastewater or surface water run-off from their home, workplace or business gets to a place of treatment and/or safe disposal to the environment. But, when the infrastructure that either transports or treats this water fails, the resultant problems can be unpleasant, costly to rectify and damaging to the environment.
Flooding & Hydrology
Flooding is the most significant disaster risk in the UK. Flooding is estimated to cost the economy about £1 billion per year. More frequent, more intense storms resulting from climate change, and inappropriate developments in floodplains will put more people and property at risk in the future and will increase the impact of flooding. It is projected that the annual cost of flooding could be up to four times higher by the end of the century.
Chemical & Process Engineering
Chemical Engineering and Process Engineering are essentially interchangeable terms, whether it is engineering chemistry to make a desired product on the industrial scale for example a pharmaceutical drug or a beer or simply process materials for some beneficial purpose for example in water treatment or renewable power generation.